chmod 400 <path-to-the-file>
chmod 400 /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
chown [new owner]:[group] <file name>
sudo chown myuser:myuser /var/mongodb_directory
mkdir [modifiers] <name of the directory>
mkdir -p /db/mongodb_data/
sudo mkdir -p /var/data
rm [options] [directory|file]
rm -rf <directory name>
ls
ls -la
cd <directory>
cat <name of the file>

rm <file name>
ps -ef | grep mongo
ps -ef | grep mongod
ps -ef | grep mongos
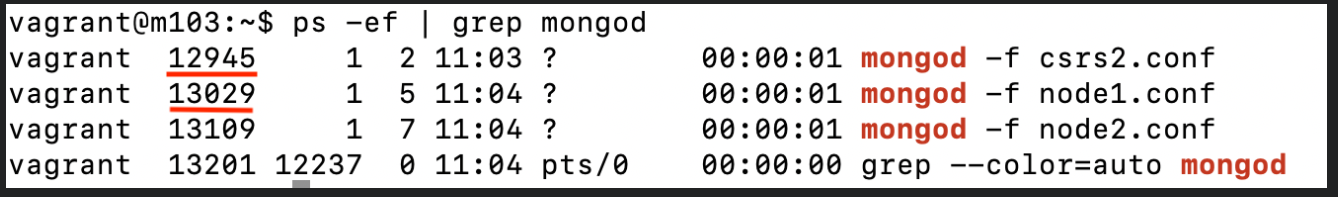
kill <pid>
kill 13029
killall mongod
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Filesystem_Hierarchy_Standard
Filesystem Hierarchy Standard - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to navigation Jump to search Linux standard for directory structure The Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS) is a reference describing the conventions used for the layout of a UNIX system. It has been made popular
en.wikipedia.org
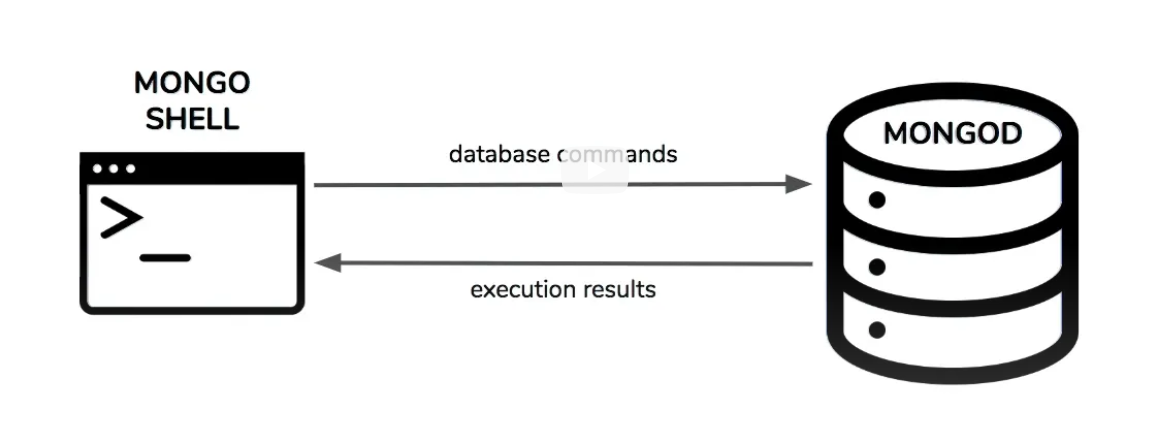
mongod
mongo
db.createCollection("employees")
use admin
db.shutdownServer()
exit
Which of these are default configurations for mongod?
- mongod listens on port 27017
- database files are stored in the directory /data/db/
mongod --help
mongod --dbpath <directory path>
mongod --port <port number>
mongod --auth
mongod --bind_ip 123.123.123.123
mongod --bind_ip localhost,123.123.123.123
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/reference/program/mongod/#bin.mongod
mongod — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB Manualmongod is the primary daemon process for the MongoDB system. It handles data requests, manages data access, and performs background management operations.This document provides a complete overview of all command line options for
www.mongodb.com
mongod
mongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/log/mongod.log
mongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/log/mongod.log --fork
mongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/log/mongod.log --fork --replSet "M103" --keyFile /data/keyfile --bind_ip "127.0.0.1,192.168.103.100" --tlsMode requireTLS --tlsCAFile "/etc/tls/TLSCA.pem" --tlsCertificateKeyFile "/etc/tls/tls.pem"
storage: dbPath: "/data/db" systemLog: path: "/data/log/mongod.log" destination: "file" replication: replSetName: M103 net: bindIp : "127.0.0.1,192.168.103.100" tls: mode: "requireTLS" certificateKeyFile: "/etc/tls/tls.pem" CAFile: "/etc/tls/TLSCA.pem" security: keyFile: "/data/keyfile" processManagement: fork: true
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/reference/program/mongod/#options
mongod — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB Manualmongod is the primary daemon process for the MongoDB system. It handles data requests, manages data access, and performs background management operations.This document provides a complete overview of all command line options for
www.mongodb.com
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/reference/configuration-options/
Configuration File Options — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB ManualThe following page describes the configuration options available in MongoDB 5.0. For configuration file options for other versions of MongoDB, see the appropriate version of the MongoDB Manual.You can configure mongod and mongos
www.mongodb.com
mongod --dbpath /data/db --logpath /data/logs --replSet M103 --bind_ip '127.0.0.1,192.168.103.100' --keyFile /data/keyfile --fork
Which of the following represents a configuration file equivalent to the command line options?
storage:
dbPath: "/data/db"
systemLog:
destination: file
path: "/data/logs"
replication:
replSetName: "M103"
net:
bindIp: "127.0.0.1,192.168.103.100"
security:
keyFile: "/data/keyfile"
processManagement:
fork: true
mongod --config mongod.conf
mongod -f mongod.conf
mongo admin --host localhost:27000 --eval '
db.createUser({
user: "m103-admin",
pwd: "m103-pass",
roles: [
{role: "root", db: "admin"}
]
})
'
Configuration File Options — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB ManualThe following page describes the configuration options available in MongoDB 5.0. For configuration file options for other versions of MongoDB, see the appropriate version of the MongoDB Manual.You can configure mongod and mongos
www.mongodb.com
ls -l /data/db
ls -l /data/db/diagnostic.data
ls -l /data/db/journal
ls /tmp/mongodb-27017.sock
Which of the following files in the MongoDB data directory can you access to view collection data?
- The correct answer is none of the above. You should never access the data files directly.
mkdir -p /var/mongodb/db
mongo admin --host localhost:27000 --eval '
db.createUser({
user: "m103-admin",
pwd: "m103-pass",
roles: [
{role: "root", db: "admin"}
]
})
'
mongod --config mongod.conf --dbpath /var/mongodb/db --port 27000
Explain Results — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB ManualTo return information on query plans and execution statistics of the query plans, MongoDB provides:The explain results present the query plans as a tree of stages."winningPlan" : { "stage" : , ... "inputStage" : { "stage" : , ..
www.mongodb.com
db.createUser()
db.dropUser()
db.<collection>.renameCollection()
db.<collection>.createIndex()
db.<collection>.drop()
db.dropDatabase()
db.createCollection()
db.serverStatus()
db.runCommand({
"createIndexes":"<collection_name>",
"indexes":[
{
"key":{ "product": 1 },
"name": "name_index"
}
]
}
)
db.<collection>.createIndex(
{ "product": 1 },
{ "name": "name_index" }
)
db.<collection>.createIndex
Which of the following methods executes a database command?
- db.runCommand( { <COMMAND> } )
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/release-notes/4.2/#logging-and-diagnostics
Release Notes for MongoDB 4.2 — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB ManualIssues fixed in 4.2.20:Issues fixed in 4.2.19:SERVER-62065 Upgrade path from 3.6 to 4.0 can leave chunk entries without history on the shardsSERVER-60685 TransactionCoordinator may interrupt locally executing update with non-Int
www.mongodb.com
mongo admin --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --eval ' db.getLogComponents() '
mongo admin --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --eval ' db.setLogLevel(0, "index") '
db.adminCommand({ "getLog": "global" })
tail -f /data/db/mongod.log
mongo admin --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --eval ' db.products.update( { "sku" : 6902667 }, { $set : { "salePrice" : 39.99} } ) '
grep -i 'update' /data/db/mongod.log
Which of the following operations can be used to access the logs?
- Running db.adminCommand({ "getLog": "global" }) from the Mongo shell
- Running tail -f <path-to-log-file> from the command line
db.runCommand({listCollections: 1})
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.getProfilingLevel() '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.setProfilingLevel(1) '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.getCollectionNames() '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.setProfilingLevel( 1, { slowms: 0 } ) '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.new_collection.insert( { "a": 1 } ) '
mongo newDB --host 192.168.103.100:27000 -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin --eval ' db.system.profile.find().pretty() '
Which of the following events are captured by the profiler?
- Administrative operations
- CRUD operations
- Configuration operations
mongod --config mongod.conf --dbpath /var/mongodb/db --port 27000 --logpath /var/mongodb/logs/mongod.log --fork
mongod -f mongod.conf --port 27000 --auth
cat /etc/mongod.conf
mongod -f /etc/mongod.conf
mongo --host 127.0.0.1:27017
use admin
db.createUser({
user: "root",
pwd: "root123",
roles : [ "root" ]
})
mongo --username root --password root123 --authenticationDatabase admin
db.stats()
use admin
db.shutdownServer()
When should you deploy a MongoDB deployment with security enabled?
- When deploying a development environment
- When deploying your staging environment
- When deploying an evaluation environment
- When deploying your production environment
https://university.mongodb.com/courses/M310/about
Free MongoDB Official Courses | MongoDB University
We have new content available. This course has been retired. MongoDB University continuously monitors industry trends and revises our courses to keep pace with changes in technology. To ensure that we offer you the most relevant training opportunities, we
university.mongodb.com
mongo admin -u root -p root123
db.createUser(
{ user: "security_officer",
pwd: "h3ll0th3r3",
roles: [ { db: "admin", role: "userAdmin" } ]
}
)
db.createUser(
{ user: "dba",
pwd: "c1lynd3rs",
roles: [ { db: "admin", role: "dbAdmin" } ]
}
)
db.grantRolesToUser( "dba", [ { db: "playground", role: "dbOwner" } ] )
db.runCommand( { rolesInfo: { role: "dbOwner", db: "playground" }, showPrivileges: true} )
Which of the following actions are granted to the userAdmin built-in role?
- dropRole
- createRole
- viewUser
Which of the following are true about replication in MongoDB?
- In the event of failover, the nodes vote to elect a new primary.
- The secondary nodes replicate data from the primary node.
http://thesecretlivesofdata.com/raft/
Raft
thesecretlivesofdata.com
Raft Consensus Algorithm
What is Raft? Raft is a consensus algorithm that is designed to be easy to understand. It's equivalent to Paxos in fault-tolerance and performance. The difference is that it's decomposed into relatively independent subproblems, and it cleanly addresses all
raft.github.io
replica sets in MongoDB?
- Replica set members have a fixed role assigned.
- We should always use arbiters.
- We can have up to 50 voting members in a replica set.
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node1
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27011
security:
authorization: enabled
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node1/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-example
sudo mkdir -p /var/mongodb/pki/
sudo chown vagrant:vagrant /var/mongodb/pki/
openssl rand -base64 741 > /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
chmod 400 /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
mkdir -p /var/mongodb/db/node1
mongod -f node1.conf
cp node1.conf node2.conf
cp node2.conf node3.conf
vi node2.conf
:wq
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node2
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27012
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node2/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-example
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node3
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27013
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node3/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-example
mkdir /var/mongodb/db/{node2,node3}
mongod -f node2.conf
mongod -f node3.conf
mongo --port 27011
rs.initiate()
use admin
db.createUser({
user: "m103-admin",
pwd: "m103-pass",
roles: [
{role: "root", db: "admin"}
]
})
exit
mongo --host "m103-example/192.168.103.100:27011" -u "m103-admin"
-p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"
rs.status()
rs.add("m103:27012")
rs.add("m103:27013")
rs.isMaster()
rs.stepDown()
rs.isMaster()
about setting up a replica set
- rs.initiate() must be run on every node in the replica set.
- Enabling internal authentication in a replica set implicitly enables client authentication.
Chapter 2: Replication
Lab: Deploy a Replica Set
mongod --replSet m103-repl --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/1 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 27001 --auth
mongod --replSet m103-repl --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/2 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 27002 --auth
mongod --replSet m103-repl --dbpath /var/mongodb/db/3 --keyFile /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile --port 27003 --auth
rs.initiate()
db.createUser({ user: "m103-admin", pwd: "m103-pass", roles: [ {role: "root", db: "admin"} ] })
mongo admin -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --port 27001
use admin
rs.add("localhost:27002")
rs.add("localhost:27003")
12 total, 12 passed, 0 skipped:
[PASS] "localhost:27001 is running"
[PASS] "localhost:27002 is running"
[PASS] "localhost:27003 is running"
[PASS] "Replication is enabled on localhost:27001"
[PASS] "Replication is enabled on localhost:27002"
[PASS] "Replication is enabled on localhost:27003"
[PASS] "Replica set 'm103-repl' has the correct name"
[PASS] "The replica set 'm103-repl' contains localhost:27001"
[PASS] "The replica set 'm103-repl' contains localhost:27002"
[PASS] "The replica set 'm103-repl' contains localhost:27003"
[PASS] "The replica set enforces client authentication"
[PASS] "The replica set m103-repl uses keyfile authentication"
Which of the following fields are included in the replica set configuration document?
- version
- members
- _id
rs.status()
rs.isMaster()
db.serverStatus()['repl']
rs.printReplicationInfo()
What information can be obtained from running rs.printReplicationInfo()?
- The time of the latest entry in the oplog.
- The time of the earliest entry in the oplog.
mkdir allbymyselfdb
mongod --dbpath allbymyselfdb
mongo
show dbs
use local
show collections
use local
db.oplog.rs.find()
var stats = db.oplog.rs.stats()
stats.capped
stats.size
stats.maxSize
rs.printReplicationInfo()
Chapter 2: Replication
Local DB: Part 2
use m103 db.createCollection('messages')
use local
db.oplog.rs.find( { "o.msg": { $ne: "periodic noop" } } ).sort( { $natural: -1 } ).limit(1).pretty()
use m103
for ( i=0; i< 100; i++) { db.messages.insert( { 'msg': 'not yet', _id: i } ) }
db.messages.count()
use local
db.oplog.rs.find({"ns": "m103.messages"}).sort({$natural: -1})
use m103
db.messages.updateMany( {}, { $set: { author: 'norberto' } } )
use local
db.oplog.rs.find( { "ns": "m103.messages" } ).sort( { $natural: -1 } )
- The oplog.rs collection contains all operations that will be replicated.
- The local database will not be replicated.
Chapter 2: Replication
Reconfiguring a Running Replica Set
node4.conf
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node4
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27014
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node4/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-example
arbiter.conf
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/arbiter
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 28000
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/arbiter/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-example
mongod -f node4.conf
mongod -f arbiter.conf
rs.add("m103:27014")
rs.addArb("m103:28000")
rs.isMaster()
rs.remove("m103:28000")
cfg = rs.conf()
cfg.members[3].votes = 0
cfg.members[3].hidden = true
cfg.members[3].priority = 0
rs.reconfig(cfg)
about reconfiguring a replica set with rs.reconfig()?
- It does not require any of the nodes to restarted.
- It does not require any of the configuration files to be updated.
mongo admin -u m103-admin -p m103-pass --port 27001
cfg = rs.conf()
cfg.members[3].votes = 0
cfg.members[3].hidden = true
cfg.members[3].priority = 0
rs.reconfig(cfg)
3 total, 3 passed, 0 skipped:
[PASS] "localhost:27004 has zero (0) votes"
[PASS] "localhost:27004 is hidden"
[PASS] "localhost:27004 has priority zero (0)"
Chapter 2: Replication
Reads and Writes on a Replica Set
mongo --host "m103-example/m103:27011" -u "m103-admin" -p
"m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"
rs.isMaster()
use newDB
db.new_collection.insert( { "student": "Matt Javaly", "grade": "A+" } )
mongo --host "m103:27012" -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass"
--authenticationDatabase "admin"
show dbs
rs.slaveOk()
use newDB
db.new_collection.find()
db.new_collection.insert( { "student": "Norberto Leite", "grade": "B+" } )
use admin
db.shutdownServer()
mongo --host "m103:27011" -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass"
--authenticationDatabase "admin"
rs.isMaster()
about reading and writing from secondaries?
- We have to run rs.slaveOk() before we can read from secondary nodes.
Chapter 2: Replication
Failover and Elections
cfg = rs.conf()
cfg.members[2].priority = 0
rs.reconfig(cfg)
rs.isMaster()
rs.stepDown()
rs.isMaster()
Which of the following is true about elections?
- Nodes with priority 0 cannot be elected primary.
- Nodes with higher priority are more likely to be elected primary.
Chapter 2: Replication
Write Concerns: Part 1
Write Concerns: Part 2
Consider a 3-member replica set, where one secondary is offline. Which of the following write concern levels can still return successfully?
- majority
Chapter 2: Replication
Lab - Writes with Failovers
Problem:
Evaluate the effect of using a write concern with a replica set where one node has failed.
Consider a 3-node replica set with only 2 healthy nodes, that receives the following insert() operation:
use payroll
db.employees.insert(
{ "name": "Aditya", "salary_USD": 50000 },
{ "writeConcern": { "w": 3, "wtimeout": 1000 } }
)
Which of the following is true about this write operation?
- The unhealthy node will receive the new document when it is brought back online.
- If a writeConcernError occurs, the document is still written to the healthy nodes.
Chapter 2: Replication
Read Concerns
Which of the following read concerns only return data from write operations that have been committed to a majority of nodes?
- linearizable
- majority
Chapter 2: Replication
Read Preferences
Which of the following read preference options may result in stale data?
- nearest
- primaryPreferred
- secondaryPreferred
Chapter 2: Replication
Lab: Read Preferences
Consider a 3-node replica set that experiences a network outage.
Two of the three nodes were unreachable during the outage, leaving one node remaining.
Which of these readPreferences will allow you to read data from this node?
- primaryPreferred
- secondaryPreferred
- nearest
- secondary
Chapter 3: Sharding
When to Shard
We should consider sharding when:
- we are holding more than 5TB per server and operational costs increase dramatically.
- government regulations require data to be located in a specific geography.
- our organization outgrows the most powerful servers available, limiting our vertical scaling options.
Chapter 3: Sharding
Sharding Architecture
In a sharded cluster, collection metadata is stored in:
- the configuration servers.
Chapter 3: Sharding
Setting Up a Sharded Cluster
Configuration file for first config server
csrs_1.conf
sharding:
clusterRole: configsvr
replication:
replSetName: m103-csrs
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.103.100
port: 26001
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/csrs1.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/csrs1
csrs_2.conf
sharding:
clusterRole: configsvr
replication:
replSetName: m103-csrs
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.103.100
port: 26002
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/csrs2.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/csrs2
csrs_3.conf
sharding:
clusterRole: configsvr
replication:
replSetName: m103-csrs
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.103.100
port: 26003
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/csrs3.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/csrs3
Starting the three config servers:
mongod -f csrs_1.conf
mongod -f csrs_2.conf
mongod -f csrs_3.conf
Connect to one of the config servers:
mongo --port 26001
Initiating the CSRS:
rs.initiate()
Creating super user on CSRS:
use admin
db.createUser({
user: "m103-admin",
pwd: "m103-pass",
roles: [
{role: "root", db: "admin"}
]
})
Authenticating as the super user:
db.auth("m103-admin", "m103-pass")
Add the second and third node to the CSRS:
rs.add("192.168.103.100:26002")
rs.add("192.168.103.100:26003")
Mongos config (mongos.conf):
sharding:
configDB: m103-csrs/192.168.103.100:26001,192.168.103.100:26002,192.168.103.100:26003
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.103.100
port: 26000
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/mongos.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
Start the mongos server:
mongos -f mongos.conf
Connect to mongos:
vagrant@m103:~$ mongo --port 26000 --username m103-admin --password m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin
Check sharding status:
MongoDB Enterprise mongos> sh.status()
Updated configuration for node1.conf:
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node1
wiredTiger:
engineConfig:
cacheSizeGB: .1
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27011
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node1/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-repl
Updated configuration for node2.conf:
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node2
wiredTiger:
engineConfig:
cacheSizeGB: .1
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27012
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node2/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-repl
Updated configuration for node3.conf:
sharding:
clusterRole: shardsvr
storage:
dbPath: /var/mongodb/db/node3
wiredTiger:
engineConfig:
cacheSizeGB: .1
net:
bindIp: 192.168.103.100,localhost
port: 27013
security:
keyFile: /var/mongodb/pki/m103-keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/mongodb/db/node3/mongod.log
logAppend: true
processManagement:
fork: true
replication:
replSetName: m103-repl
Connecting directly to secondary node (note that if an election has taken place in your replica set, the specified node may have become primary):
mongo --port 27012 -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"
Shutting down node:
use admin
db.shutdownServer()
Restarting node with new configuration:
mongod -f node2.conf
Stepping down current primary:
rs.stepDown()
Adding new shard to cluster from mongos:
sh.addShard("m103-repl/192.168.103.100:27012")
What is true about the mongos?
- The mongos configuration file doesn't need to have a dbpath.
- The mongos configuration file needs to specify the config servers.
Chapter 3: Sharding
Lab: Deploy a Sharded Cluster
mongo --port 26000 -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin"
sh.addShard("shard1/localhost:27001")
2 total, 2 passed, 0 skipped:
[PASS] "mongos is running"
[PASS] "shard1 has been added to cluster"
Chapter 3: Sharding
Config DB
use config
db.databases.find().pretty()
db.collections.find().pretty()
db.shards.find().pretty()
db.chunks.find().pretty()
db.mongos.find().pretty()
When should you manually write data to the Config DB?
- When directed to by MongoDB documentation or Support Engineers
Chapter 3: Sharding
Shard Keys
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/sharding-shard-key/#change-a-document-s-shard-key-value
Shard Keys — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB ManualThe shard key is either a single indexed field or multiple fields covered by a compound index that determines the distribution of the collection's documents among the cluster's shards.MongoDB divides the span of shard key values
www.mongodb.com
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/sharding-shard-key/#refine-a-shard-key
Shard Keys — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB ManualThe shard key is either a single indexed field or multiple fields covered by a compound index that determines the distribution of the collection's documents among the cluster's shards.MongoDB divides the span of shard key values
www.mongodb.com
use m103
show collections
sh.enableSharding("m103")
db.products.findOne()
db.products.createIndex( { "sku": 1 } )
sh.shardCollection( "m103.products", { "sku": 1 } )
sh.status()
Which of the following statements is true about shard keys?
- Shard keys are used to route queries to specific shards
- Shard keys must be supported by an index
Chapter 3: Sharding
Picking a Good Shard Key
Which of the following are indicators that a field or fields are a good shard key choice?
- Low Frequency
- High Cardinality
- Non-monotonic change
Chapter 3: Sharding
Hashed Shard Keys
Which of the following functions does Hashed Sharding support?
- Even distribution of a monotonically changing shard key field
Chapter 3: Sharding
Lab: Shard a Collection
mongoimport /dataset/products.json -d m103 -c products --drop --port 26000 --username m103-admin --password m103-pass --authenticationDatabase admin
sh.enableSharding("m103")
db.products.createIndex({"name": 1})
db.adminCommand( { shardCollection: "m103.products", key: { name: 1 } } )
sh.status()
validate_lab_shard_collection
sh.addShard("m103-repl-2/localhost:27004")
2 total, 2 passed, 0 skipped:
[PASS] "The dataset is imported to m103.products"
[PASS] "m103.products uses the correct shard key"
Chapter 3: Sharding
Chunks
use config
show collections
db.chunks.findOne()
use config
db.settings.save({_id: "chunksize", value: 2})
sh.status()
mongoimport /dataset/products.part2.json --port 26000 -u "m103-admin" -p "m103-pass" --authenticationDatabase "admin" --db m103 --collection products
Which of the following is true about chunks?
- Chunk ranges have an inclusive minimum and an exclusive maximum.
Chapter 3: Sharding
Lab: Documents in Chunks
Consider the following document:
{
"_id" : ObjectId("573f7197f29313caab89b3a4"),
"sku" : 20005012,
"name" : "Complete Hit Singles A's & B's - CD",
"type" : "Music",
"regularPrice" : 14.99,
"salePrice" : 14.99,
"shippingWeight" : "0.25"
}
Which of the following chunks would contain this document?
{
"_id" : "m103.products-sku_20000000",
"shard" : "shard2",
"min" : {
"sku" : 20000000
},
"max" : {
"sku" : 25000000
}
}
Chapter 3: Sharding
Balancing
Manage Sharded Cluster Balancer — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB ManualChanged in version 3.4: The balancer process has moved from the mongos instances to the primary member of the config server replica set.This page describes common administrative procedures related to balancing. For an introducti
www.mongodb.com
sh.startBalancer(timeout, interval)
sh.stopBalancer(timeout, interval)
sh.setBalancerState(boolean)
Given a sharded cluster running MongoDB 3.6, which of the shard components is responsible for running the Balancer process?
- Primary node of the Config Server Replica Set
Chapter 3: Sharding
Queries in a Sharded Cluster
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/aggregation-pipeline-sharded-collections/
Aggregation Pipeline and Sharded Collections — MongoDB Manual
Docs Home → MongoDB ManualThe aggregation pipeline supports operations on sharded collections. This section describes behaviors specific to the aggregation pipeline and sharded collections.If the pipeline starts with an exact $match on a shard key, and t
www.mongodb.com
For a find() operation, which cluster component is responsible for merging the query results?
- The mongos that issued the query
Chapter 3: Sharding
Targeted Queries vs Scatter Gather: Part 1
db.products.find( { "sku": 20009151 } )
db.products.find( { "type": "movie" } )
{ "sku": 1, "type": 1, "name": 1 }
db.products.find( { "sku": ... } )
db.products.find( { "sku": ... , "type": ... } )
db.products.find( { "sku": ... , "type": ... , "name": ... } )
db.products.find( { "type": ... } )
db.products.find( { "name": ... } )
Chapter 3: Sharding
Targeted Queries vs Scatter Gather: Part 2
use m103
show collections
db.products.find({"sku" : 1000000749 }).explain()
db.products.find( {
"name" : "Gods And Heroes: Rome Rising - Windows [Digital Download]" }
).explain()
Given a collection that is sharded on the following shard key:
{ "sku" : 1, "name" : 1 }
Which of the following queries results in a targeted query?
- db.products.find( { "name" : "MongoHacker", "sku" : 1337 } )
- db.products.find( { "sku" : 1337, "name" : "MongoHacker" } )
- db.products.find( { "sku" : 1337 } )
Chapter 3: Sharding
Lab: Detect Scatter Gather Queries
Which of the following is required in order for a query to be targeted to a subset of shards?
- An index exists on the shard key
- The query uses the shard key
Final Exam
Final: Question 1
Which of the following are valid command line instructions to start a mongod? You may assume that all specified files already exist.
mongod -f /etc/mongod.confmongod --logpath /var/log/mongo/mongod.log --dbpath /data/db --fork
Final Exam
Final: Question 2
storage:
dbPath: /data/db
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/log/mongod.log
net:
bindIp: localhost,192.168.0.100
security:
keyFile: /var/pki/keyfile
processManagement:
fork: true
Select all the directories that MongoDB must have access to. Disregard the path to the configuration file itself, and the /tmp/ directory.
- /var/log/
- /var/pki/
- /data/db/
Final Exam
Final: Question 3
Given the following output from rs.status().members:
[
{
"_id": 0,
"name": "localhost:27017",
"health": 1,
"state": 1,
"stateStr": "PRIMARY",
"uptime": 548,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"electionTime": Timestamp(1521038358, 2),
"electionDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:39:18Z"),
"configVersion": 2,
"self": true
},
{
"_id": 1,
"name": "localhost:27018",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.517Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27022",
"configVersion": 2
},
{
"_id": 2,
"name": "localhost:27019",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.654Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27022",
"configVersion": 2
},
{
"_id": 3,
"name": "localhost:27020",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.726Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27022",
"configVersion": 2
},
{
"_id": 4,
"name": "localhost:27021",
"health": 0,
"state": 8,
"stateStr": "(not reachable/healthy)",
"uptime": 0,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(0, 0),
"t": NumberLong("-1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(0, 0),
"t": NumberLong("-1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("1970-01-01T00:00:00Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("1970-01-01T00:00:00Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.656Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:12.668Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"lastHeartbeatMessage": "Connection refused",
"configVersion": -1
},
{
"_id": 5,
"name": "localhost:27022",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:55.974Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27017",
"configVersion": 2
},
{
"_id": 6,
"name": "localhost:27023",
"health": 1,
"state": 2,
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"uptime": 289,
"optime": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDurable": {
"ts": Timestamp(1521038871, 1),
"t": NumberLong("1")
},
"optimeDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"optimeDurableDate": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:51Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.558Z"),
"lastHeartbeatRecv": ISODate("2018-03-14T14:47:56.801Z"),
"pingMs": NumberLong("0"),
"syncingTo": "localhost:27022",
"configVersion": 2
}
]
At this moment, how many replica set members are eligible to become primary in the event of the current Primary crashing or stepping down?
- 5
Final Exam
Final: Question 4
Given the following replica set configuration:
conf = {
"_id": "replset",
"version": 1,
"protocolVersion": 1,
"members": [
{
"_id": 0,
"host": "192.168.103.100:27017",
"priority": 2,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 0,
"host": "192.168.103.100:27018",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 2,
"host": "192.168.103.100:27018",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
}
]
}
What errors are present in the above replica set configuration?
- You cannot specify the same host information among multiple members.
- You cannot specify two members with the same _id.
Final Exam
Final: Question 5
Given the following replica set configuration:
conf = {
"_id": "replset",
"version": 1,
"protocolVersion": 1,
"members": [
{
"_id": 0,
"host": "localhost:27017",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 1,
"host": "localhost:27018",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 2,
"host": "localhost:27019",
"priority": 1,
"votes": 1
},
{
"_id": 3,
"host": "localhost:27020",
"priority": 0,
"votes": 0,
"slaveDelay": 3600
}
]
}
What is the most likely role served by the node with "_id": 3?
- It serves as a "hot" backup of data in case of accidental data loss on the other members, like a DBA accidentally dropping the database.
Final Exam
Final: Question 6
Given the following shard key:
{ "country": 1, "_id": 1 }
Which of the following queries will be routed (targeted)? Remember that queries may be routed to more than one shard.
db.customers.find({"country": "Norway", "_id": 54})db.customers.find({"country": { $gte: "Portugal", $lte: "Spain" }})db.customers.find({"_id": 914, "country": "Sweden"})
'푸닥거리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Two-Pizza Teams (0) | 2022.06.11 |
|---|---|
| MariaDB Galera Cluster 제약사항 (0) | 2022.06.10 |
| TLS 1.2 와 TLS 1.3 의 차이 (0) | 2022.06.02 |
| free data explore mongodb with vscode and php (0) | 2022.05.30 |
| 온라인 일방향 침해사고 대응 훈련(중급, 스피어 피싱 대응 - 기본과정) (0) | 2022.05.29 |




댓글